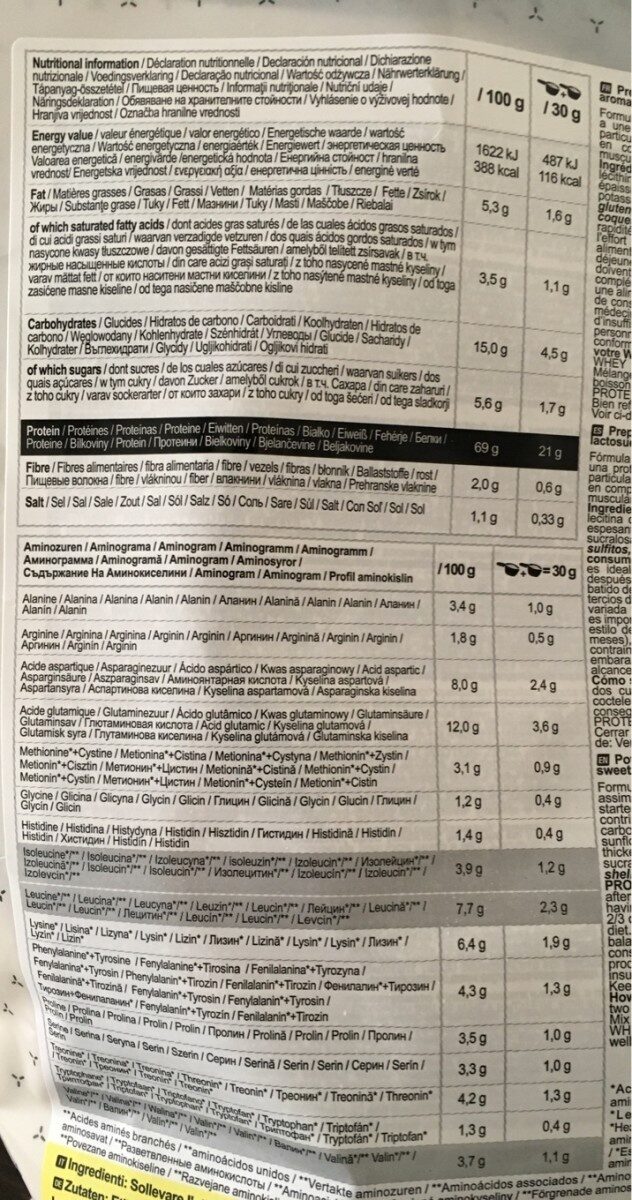
WHEY Protein Vanille - Decathlon - 900 g
This product page is not complete. You can help to complete it by editing it and adding more data from the photos we have, or by taking more photos using the app for Android or iPhone/iPad. Thank you!
×
Barra-kodea: 3608419150629 (EAN / EAN-13)
Kopurua: 900 g
Ontziratzea: en:Vacuum-packed
Markak: Decathlon
Kategoriak: Elikadura-osagarri, en:Bodybuilding supplements, en:Protein powders
Manufacturing or processing places: France
Dendak: Decathlon
Matching with your preferences
Ingurumena
Ontziratzea
Transportation
Report a problem
Datuen iturria
Product added on by kiliweb
Last edit of product page on by charlesnepote.
Produktuaren orria -gatik editatua elcoco, mannkenn, openfoodfacts-contributors, packbot, randy22, yuka.R29BRkdZVS9nOThOeXNJLzVCanM1ZlF2bU02N0FYRzRKTThKSVE9PQ, yuka.RjdGZk5vZFlpOXRXbFBkbjJrMzg5Zk5uOXJ5eGJYbWJDN1F3SUE9PQ, yuka.UTc4QVFMNGlyTlFWdmZJVXp4akV5dTRsNUphaUEwZVJLc0VESWc9PQ, yuka.UY58AcKlMZwAJ9zv1I8T7CW6BPe6McZyE24gow, yuka.VElNTlBQZ1Bpc01ncWZjRDBoM3UrdUJWeHBQeFdWaWVHZVVXSWc9PQ, yuka.VklFL0hJQUxvL29HaHRnUzVRTFkyTkp5NlphSGZEeWVJTUJNSVE9PQ, yuka.YktZdUhxWllxZHNYeDlvc3hpenM2TU53MjhYeFZqNjhjTFV6SVE9PQ, yuka.ZWJ4Y0lxME5oNklMeXNBQXhUSGN3STlUL0pyNFhWbTFPKzhLSVE9PQ.