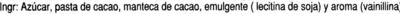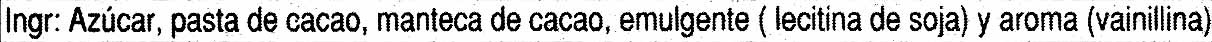Tableta de chocolate negro 45% cacao - Eureka - 200 g
This product page is not complete. You can help to complete it by editing it and adding more data from the photos we have, or by taking more photos using the app for Android or iPhone/iPad. Thank you!
×
Barra-kodea: 8410083000309 (EAN / EAN-13)
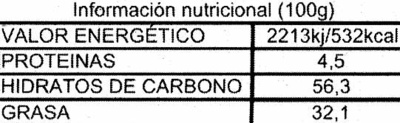
Izen arrunta: Tableta de chocolate negro con un 45% de cacao mínimo
Kopurua: 200 g
Ontziratzea: pt:Envase de papel, pt:Papel de aluminio
Markak: Eureka
Kategoriak: en:Snacks, en:Sweet snacks, en:Cocoa and its products, en:Chocolates, en:Dark chocolates, en:Extra fine dark chocolates
Etiketak, ziurtagiriak, sariak: en:Vegetarian, en:Vegan
Manufacturing or processing places: Pinto, Madrid (comunidad autónoma), España
Traceability code: ES 25.00007/M C CE, FABRICANTE Y ENVASADOR:, CHOCOLATES EUREKA S.A.
Link to the product page on the official site of the producer: http://www.chocolateseureka.com/atlantic...
Dendak: Carrefour
Saltzen diren herrialdeak: Espainia