Aceitunas pelotín con hueso sabor anchoa - Hacendado - 430 g
This product page is not complete. You can help to complete it by editing it and adding more data from the photos we have, or by taking more photos using the app for Android or iPhone/iPad. Thank you!
×
Barra-kodea: 8480000332073 (EAN / EAN-13)
Izen arrunta: Aceitunas verdes enteras sabor anchoa
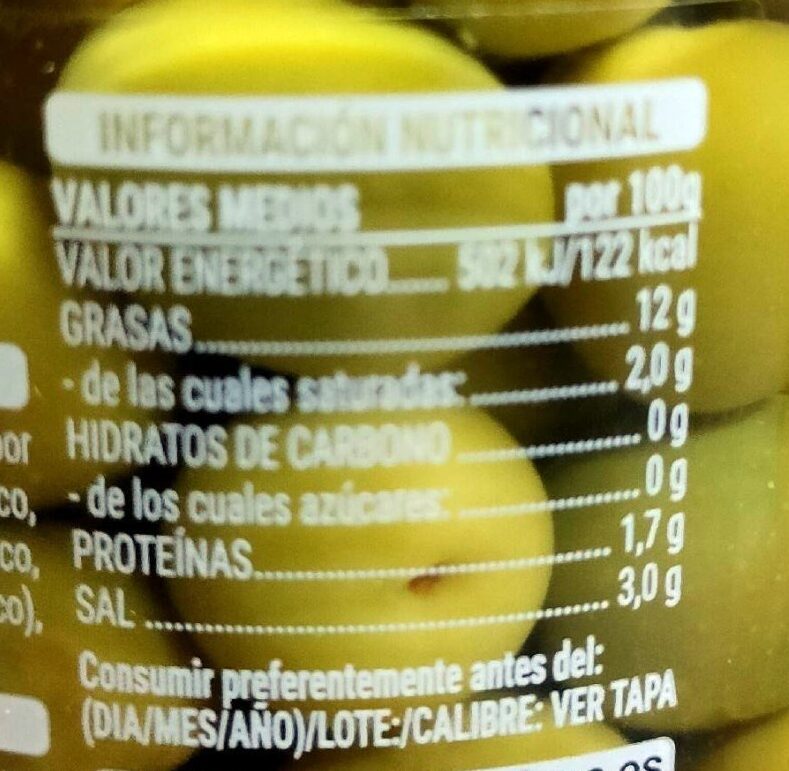
Kopurua: 430 g
Ontziratzea: es:Green dot
Markak: Hacendado
Kategoriak: en:Plant-based foods and beverages, en:Plant-based foods, en:Pickles, en:Olive tree products, en:Plant-based pickles, en:Olives, en:Green olives, en:Marinated olives, en:Whole olives, en:Whole green olives, en:Whole marinated green olives
Etiketak, ziurtagiriak, sariak:
en:Green Dot
Saltzen diren herrialdeak: Espainia
Matching with your preferences
Ingurumena
Carbon footprint
Ontziratzea
Transportation
Report a problem
Datuen iturria
Product added on by kiliweb
Last edit of product page on by roboto-app.
Produktuaren orria -gatik editatua aleene, alia, musarana, thaialagata, yuka.EupDPcOAAcY4RvDX6JAa2jzlOrrHH919Ml4Log, yuka.JpYSDt2xHvx8IvCP04ts0xrmP7a7H8JhH2ALoQ, yuka.NZFaHt7WROUTMsrMwZwr3yjjCPbsGtF2RGUCoQ, yuka.R3BKYkRwa21pY1FWaXM4dTB4VFl4WTl5K2JTRVpsbVFNTVE4SUE9PQ, yuka.WHZraEN2a2hvdE1JaHNFejNSREtxL3hZN1lhNGRFZXhJT1FTSWc9PQ, yuka.sY2b0xO6T85zoF3NwEKvlhJuTOHUojPgNh7khmesnMjfNsHIX4hVsoekY6s, yuka.sY2b0xO6T85zoF3NwEKvlktIU9Tn-iqbCQHmkEeZxOuLBJXyQ9t3vdDLMas, yuka.sY2b0xO6T85zoF3NwEKvllVVXMb-riKaDAPni2iV-dS0IpLacY4qua3HHqo, yuka.sY2b0xO6T85zoF3NwEKvlm93D9vCnGLmBSL6qG6m3PqxLZWwQ9dU8tKgF6s, yuka.sY2b0xO6T85zoF3NwEKvlmNjXPPfhyLcCCbkpXOun--eEaO2XPVL_bD7Kqs, yuka.sY2b0xO6T85zoF3NwEKvlmlsUMDVoyjpGiXtl0KizI21DrvQTMF05IPANag.