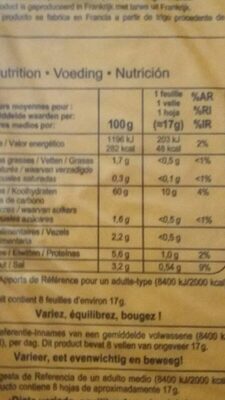
Feuilles de brick Salé Sucré - Carrefour - 136 g
This product page is not complete. You can help to complete it by editing it and adding more data from the photos we have, or by taking more photos using the app for Android or iPhone/iPad. Thank you!
×
Some of the data for this product has been provided directly by the manufacturer Carrefour.
Barra-kodea: 3560071161514 (EAN / EAN-13)
Izen arrunta: Feuilles de brick.
Kopurua: 136 g
Markak: Carrefour
Kategoriak: en:Plant-based foods and beverages, en:Plant-based foods, en:Cereals and potatoes, en:Cereals and their products, en:Pie dough, en:Brick sheets
Dendak: Carrefour
Matching with your preferences
Ingurumena
Ontziratzea
Transportation
Other information
Preparation: Pliage en samoussa : 1. Dépliez la feuille de brick. 2. Coupez-la en deux et rabattez la partie arrondie sur le bord. 3. Déposez la garniture à une extrémité. 4. Rabattez la feuille avec la farce à l'intérieur. 5. Rabattez dans l'autre sens pour former un triangle, répétez l'opération jusqu'à ce qu'il ne reste de place que pour un seul triangle. 6. Vous pouvez soit replier la dernière partie vide à l'intérieur du triangle, soit badigeonner le dernier triangle vide de jaune d'œuf battu et le rabattre. Cuisson : Vous pouvez varier les formes de vos préparations (aumônières, cigares, ...) et les faire dorer quelques minutes en surveillant bien la cuisson à la friteuse ou à la poêle dans un bain d'huile bien chaude, ou au four environ 7 min à 180°C.
Abisua: Ne pas utiliser le papier paraffiné qui se trouve entre les feuilles de brick pour la cuisson.
Conservation conditions: A conserver entre 0°C et +8°C. Afin de conserver les qualités organoleptiques de votre produit, nous vous conseillons de bien refermer le sachet après chaque utilisation.
Customer service: Interdis - TSA 91431 - 91343 MASSY Cedex - France
Report a problem
Datuen iturria
Product added on by openfoodfacts-contributors
Last edit of product page on by duhowpi.
Produktuaren orria -gatik editatua aleene, charlesnepote, kiliweb, org-carrefour, roboto-app, teolemon, yuka.J65OBPPbDpQbDt3K1t4bxRmaLdf-Jv58O3wRog, yuka.SDc0dUFwVWpsL2Nnd00xdS94VG54Tmx3M3FHeVhWTG1FK1lhSVE9PQ, yuka.VJ1sAP_aNJwuFcL9gdsR3Ru8CM7eHM97FX8Cog, yuka.sY2b0xO6T85zoF3NwEKvlhVeQ_DPjA3rNxLntWCM1tWSH5awU_tMwo_Ebqo.